Year I
First-year students have ultrasound sessions aligned with their teaching in Principles of Clinical Medicine. In addition clinical integration occurs with ultrasound added into standard patient scenario at the end of the first year.
Sessions Include:
- Ultrasound Introduction and Knobology
- Head & Neck Ultrasound
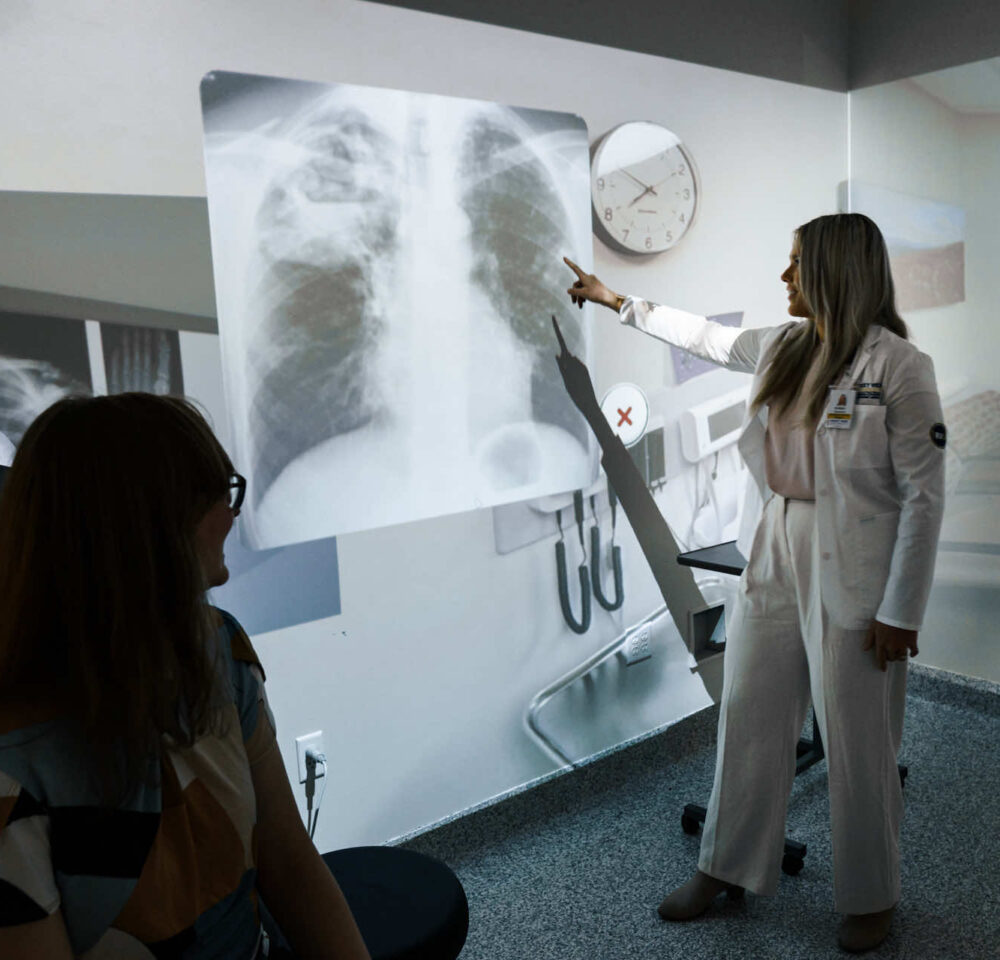
- Cardiac & Pulmonary Ultrasound
- Abdominal Ultrasound
- Musculoskeletal Ultrasound
Year II
Second-year students continue with ultrasound sessions aligned with their teaching in Principles of Clinical Medicine. Their competency exams have ultrasound component. Clinical integration occurs with ultrasound added into standard patient scenarios throughout the year.
Sessions Include:
- Review and Vascular Ultrasound
- Cardiac review and eFAST
- RUSH/ Resuscitative Ultrasound
- GI/GU Ultrasound
- Musculoskeletal Ultrasound
- Procedural Workshop
Year III and IV
Third and fourth year students have the opportunity to attend training in ultrasound activities through rotations and preparatory classes for rotations. In addition elective experiences are being planned.